1675 Picard Creates 1st Light
The Evolution
of
Time Line
The technology behind creating light dates back
before the actual age of electrical experimentation, long
before Edison’s time.
It was the year 1675 when the French astronomer “Jean Picard”
observed a glow in a glass mercury barometer tube.
when the tube was shaken and a glow called “Barometric
Light” occurred. The actual cause of the light is static electricity.
Even though the cause of barometric light was not understood,
it was still investigated. Later, when the principles of electricity
were discovered, scientists were able to move forward towards the
invention of many forms of lighting, and eventually, neon lighting.
Heinrich Geissler’s Glowing Glass Tubes
In 1855 Heinrich Geissler developed a sealed glass tubes with two electrodes,
and running an electric current thru it making the gas in the tube
glow. He devised his famous mercury air pump which would later
contribute to the success of Thomas Edison's first incandescent
lamps in 1879
Geissler began experimenting with what were later to become
known as the 'Geissler tube' and full-scale production of
these were well underway in the 1880s. An electrical discharge
through a partially evacuated tube glows with a color depending
on the type of glass in the tube and the gas inside.
1855

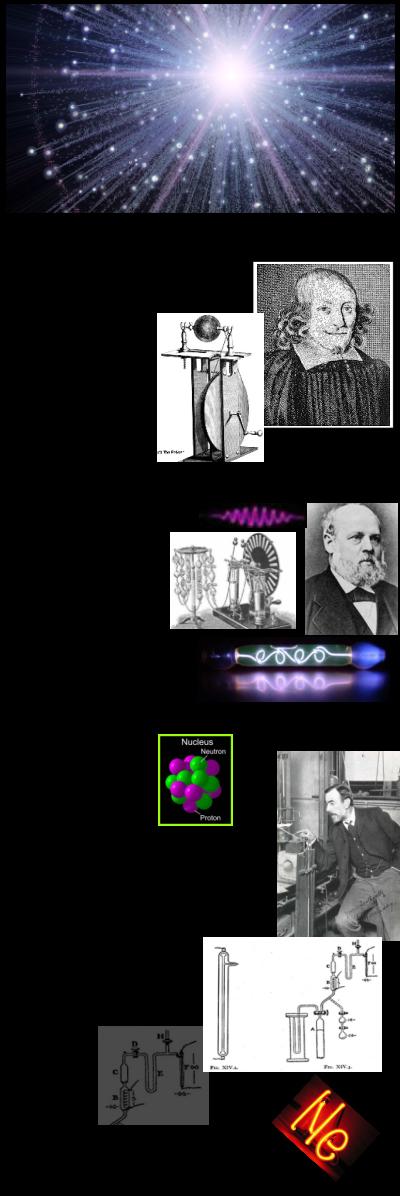
In 1894 Sir William Ramsay’s discovers Argon and then isolates
Helium . He had found the first and the third member of the group
of inert gases (Helium and Argon). Ramsay seeks the assistance
of Morris W. Travers and they searched for and found the member
element Krypton. They then solidified some of their fifteen liters of
Argon by surrounding it with liquid air boiling under reduced pressure.
The result was a light with a complex spectra with many lines in red,
a number of faint green, and some in violet. The yellow line is fairly
bright, and persists at very high vacuum. This was the element they
had been searching for. Ramsay maintaining the chemical family's
name and called it "Neon". Sir William Ramsay got the Nobel
Prize for Chemistry in 1904 because of his discovery of four of
the noble gases (Neon, Argon, Krypton, and Xenon) which
eventually led him to his discovery of Neon.
The word neon comes from the Greek "neos," meaning
"the new gas." Neon is a rare gaseous element present in the
atmosphere to the extent of 1 part in 65,000 of air.
Neon can be obtained by liquefaction of air and separated
from the other gases by a process called fractional distillation.
1894 Sir William Ramsay Discovers the Chemical Element - Neon
Jean Picard
French Astronomer
Heinrich Geissler
German Glassblower & Physicist
Sir William Ramsay
British Chemist
Name: Neon
Symbol: Ne
Atomic Number: 10
Atomic Mass: 20.1797 amu
Melting Point: -248.6 °C (-415.48 °F)
Boiling Point: -246.1 °C (-410.98 °F)
Number of Protons/Electrons: 10
Number of Neutrons: 10
Classification: Noble Gas
Crystal Structure: Cubic
Density @ 293 K: 0.901 g/cm3
Color: colorless


